Federation Platform and Privacy Waves: How Meta distributes compliance-related tasks at scale

- We’re exploring Meta’s Federation Platform, a scalable set of tools for managing compliance-related tasks, along with Privacy Waves, our method for batching these tasks and ensuring accountability.
- Together, the Federation Platform and Privacy Waves create a structured, effective, and sustainable approach to operationalizing privacy work, enabling Meta to safeguard user data for the billions of people that use our products.
- Given its success in the privacy domain, we’re expanding this approach to other domains such as security and accessibility.
At Meta, we take a systematic approach to privacy-related compliance. Experts decode complex obligations into actionable product requirements, ensuring coverage and consistency across all Meta products. We then deploy technical solutions that address these requirements at scale through our Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) initiative. Following that, our privacy teams centrally automate remediation of potential issues; and finally, if expert help is needed, they send tasks to product teams for distributed execution.
Operationalizing this work at Meta’s scale – across tens of thousands of engineers and numerous products – requires robust coordination. To facilitate this, we developed the Federation Platform and Privacy Waves program:
- The Federation Platform breaks down large compliance-related initiatives into smaller, manageable workstreams. It distributes tasks to the appropriate teams and enables them to track progress through to completion.
- The Privacy Waves program organizes tasks for these initiatives into monthly batches, creating a predictable cadence that improves quality and accountability of task distribution and management. It helps teams plan and execute their compliance-related work systematically, rather than reactively.
Together, the Federation Platform and Privacy Waves program play a critical role in safeguarding user data and ensuring consistent, effective operations of our systems and solutions, supporting Meta’s compliance posture (for both existing and future obligations) while balancing internal engineering efficiency and experience.
They are significant levers in Meta’s compliance-related efforts, managing over 100,000 tasks annually within established timelines. Internal surveys reveal significantly higher positive sentiment for Privacy Waves tasks compared to ad-hoc tasks. And we estimate that the program has saved hundreds of thousands of engineering hours by enhancing strategy, tooling, and task quality. The success of this approach in the privacy domain has encouraged its expansion into other domains such as security, accessibility and our broader compliance efforts.
The need for a centralized work distribution and management system
There are several reasons why large organizations like Meta benefit from a centralized system to distribute and manage compliance-related work:
- Meeting privacy obligations at scale is complex because it often requires thousands of engineers to each complete small, specialized tasks across hundreds of global pressures and thematic areas.
- Scalability and internal accountability are crucial. Doing this ad hoc can lead to task fatigue, difficulty meeting completion expectations, and diminished developer sentiment. Without centralized management and oversight, it becomes challenging to effectively prioritize, track, and execute work across organizational boundaries, or to deduplicate tasks across teams.
- Developer experience matters and can even increase output. A positive, well-managed task flow reduces operational burden, maintains morale, and sustains high productivity.
- External accountability is essential to operations. Meta must demonstrate consistent and effective operations to regulators and auditors. The Federation Platform enables clear, standardized practices along with consistent documentation and validation to uphold Meta’s compliance posture in response to external requirements.
Managing privacy work with the Federation Platform
Workstream configuration: How engineers integrate with the platform
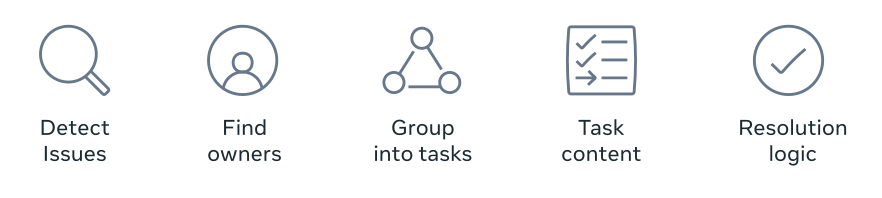
Implementing a workstream on the Federation Platform requires defining in-code logic that mirrors the typical lifecycle of a potential privacy issue. This involves specifying how to detect, distribute, remediate, and verify resolution of these issues, ensuring their effective management. The resulting technical workstream configuration (code file) includes methods for:
- Scraping flags: Scraping involves identifying the relevant set of privacy flags – indications of potential issues that require attention. These flags are ingested into the Federation Platform based on the workstream’s configuration, which often leverages Meta’s reusable detection and verification frameworks. The scraping process can be automated to run daily using in-code methods or ad-hoc via the platform’s intake APIs. Scraping defines the scope of the workstream, with additional filters and linters configured as needed.
- Ownership resolution: This involves implementing logic to determine the ownership of privacy flags. Typically, this requires referencing Meta’s central catalog to map relevant assets, such as code files and data tables, to their respective owners.
- Grouping: Workstreams can optionally group related flags, such as those with a common owner or located in the same directory. This allows for efficient bulk remediation by bundling these flags into a single task or diff (code change).
- Actioning (Task/Diff): Workstreams decide how to address each privacy flag or group of flags. The most common approach is to file a task, which is then assigned to the asset owner. Alternatively, they can choose to send automated code changes to directly resolve issues, which must be reviewed by the asset owner.
- Task content and distribution: Workstreams configure the content of tasks, providing context on why the task is necessary, its alignment with privacy initiatives, and instructions and workflows to fix the issue. Workstreams also configure how they want to distribute their tasks, which is most commonly done through the Privacy Waves program.
- Resolution logic: Finally, workstreams define resolution logic to determine when a privacy flag is resolved. This allows the Federation Platform to automatically close tasks once the underlying issue is fixed or reopen tasks if they are prematurely closed.
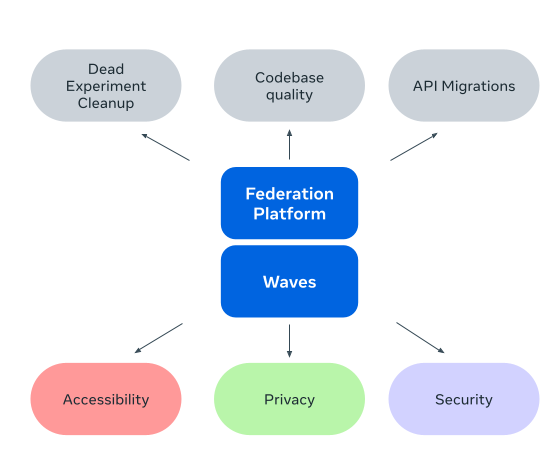
The general-purpose configuration described above is versatile and extends well beyond privacy use cases. For instance, security and accessibility workstreams have started utilizing it to address potential vulnerabilities and product accessibility matters through task distribution. Similarly, engineering excellence initiatives operate workstreams to drive API migrations, code quality improvements, and the cleanup of obsolete experiments across numerous teams. This positions the Federation Platform as a powerful tool for driving diverse, large scale initiatives across the organization.
In addition to the technical configuration steps outlined above, privacy workstreams strive to adhere to the comprehensive end-to-end federation process detailed below, ensuring a holistic approach to managing privacy issues.
An overview of the end-to-end federation process
Step 1: High-level strategy and planning
Before distributing work, a thorough review process evaluates the holistic strategy for a privacy area to ensure their plan efficiently meets applicable privacy-related obligations. This strategy often involves a combination of developing privacy aware infrastructure and controls through traditional project work, privacy teams centralizing bulk remediation via scripts and mass code changes, and – when automated solutions are not feasible – distributing work across the company via Federation Platform workstreams and Privacy Waves.
Product organizations (e.g., Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp) receive advanced visibility into upcoming privacy work, allowing them to incorporate it into their roadmaps and commit to its delivery. While aligning work across organizational lines takes longer, it ultimately enables easier and more efficient completion of tasks.
Step 2: Configuring efficient task experiences
Tasks for Federation Platform workstreams that participate in Privacy Waves must clearly communicate the nature of the work, due dates, link to relevant context and documentation, and contain the necessary steps for resolution. Structured tasks guide users through a wizard-like workflow with multiple-choice questions, often culminating in automated remediations (e.g., code changes, click-to-fix tools) based on user decisions. These ‘wizards’ facilitate appropriate decision-making by product engineers and, in some cases, have been shown to reduce the effort required to complete tasks by around 50%.
Tasks are enriched with links to support forums and similar tasks where assistance can be sought, if needed. AI-powered support agents are embedded within tasks which help task owners search through relevant resources and write code quickly, which requires human review before landing.
Step 3: Reviewing and improving task quality
A review committee provides feedback on task quality and content for workstreams participating in Privacy Waves, identifying areas for improvement and opportunities for automation. Automated health signals for each workstream, such as completion rates, open tasks, deferral rates, and developer friction (e.g., broken tooling, inadequate support), are measured and tracked. Workstreams and their reviewers monitor these metrics monthly and are held accountable for improvements.
Engineering sentiment is captured for each workstream through task owner surveys, and AI is used to summarize their feedback, enabling workstream owners to learn from task owner input and enhance future tasks. These features contribute to improved work quality, developer sentiment, and completion rates.
Step 4: Distributing the work
Linting tools are employed to prevent the distribution of low-quality and low-risk work (e.g., for assets queued for deletion or lacking any data). Workstreams can configure the lints they wish to apply.
Tasks are sent in Privacy Waves, which are batches of privacy-related work distributed at a predefined, predictable cadence. Privacy Waves streamline execution, coordination, and reporting, since all tasks in a wave share the same deadline, allowing for timely reminders.
A sophisticated matching algorithm aligns tasks with teams based on competing priorities related to assets they own. Combined with predictable task distribution, this approach ensures timely work assignment and enables teams to effectively prioritize, allowing them to balance responsibilities and make consistent progress towards addressing their workloads.
Step 5: Ensuring accountability of execution
To ensure timely completion of tasks, deadlines are established with an aim at preventing deferral beyond these critical dates. Automated nudges and escalations are strategically used to remind individuals and teams to complete work on schedule, minimizing unnecessary noise and highlighting overdue tasks that require immediate attention.
Furthermore, completion rates for privacy work are rigorously measured and reported at all organizational levels, fostering a culture of accountability from frontline teams to leadership. This transparent approach ensures that everyone is held responsible for executing their tasks in a timely manner, promoting a sense of ownership and urgency across the organization.
Step 6: Reporting and recognition
The centralized distribution of tasks via Federation Platform and Privacy Waves streamline operational effectiveness and verification. These systems document completed tasks in a standardized format that aligns with expectations, providing clear and consistent evidence that supports Meta’s compliance posture in response to external requirements.
At Meta, executing on compliance-related work is an integral part of internal engineering expectations. To ensure that individuals receive the recognition they deserve, centralized recognition tooling is utilized to credit their contributions in performance evaluations. This approach not only motivates engineers to prioritize these efforts, but also reinforces the importance of this critical work in maintaining user trust and our compliance posture.
Expansions for the Federation Platform and Waves
As Meta continues to evolve, the Federation Platform and Waves programs are actively being expanded into new domains like security, accessibility, and broader compliance-related efforts. This expansion presents unique challenges, including different types of tasks, complex multi-step remediation processes, varying deadlines, and more. However, our foundational principles of centralized task distribution, execution tracking, and accountability provide a robust framework to address these challenges effectively.
To ensure seamless extension into new areas, we’ll refine our tooling and processes, developing solutions that cater to each domain’s specific needs while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency. By doing so, we aim to exceed expectations, reinforcing our commitment to safeguarding user data and ensuring efficient and consistent operations across all areas. This forward-looking approach underscores Meta’s dedication to innovation in compliance standardization, setting a benchmark for other tech companies to follow.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express our gratitude to reviewers of this post, including (in last name alphabetical order): Chris Adams, Bob Baldwin, Denys Besedynskyy, Herb David, Dylan Drop, Katriel Cohn-Gordon, Xenia Habekoss, Mohit Jha, Ryan Pratt, Matt Pregozen, Jessica Retka, Thomas Richards, and Chris Wiltz, many of whom have made significant contributions to Federation Platform and Privacy Waves.
Additionally, we would also like to acknowledge the contributions of many current and former Meta employees, who have played a crucial role in developing and maturing Federation Platform and Privacy Waves over the years. In particular, we would like to extend special thanks to (in last name alphabetical order): Quinn Armstrong, Gunnar Arnesen, Cecilia Baek, Yashdeep Bindal, Chris Buckley, Adam Campbell, Katriel Cohn-Gordon, Ruo Ding, Jason Fennell, Andrew Fong, Riccardo Govoni, Abhishek Gulati, Tucker Hart, Aleksandar Ilic, AJ Jahansouz, Shruthi Katakam, Risa Kawai, Bruce Liu, Emile Litvak] Amira Malpass, Idan Michael, Jason Nawrocki, Anthony O’Sullivan, Yuval Oren, Disha Parekh, Uday Patireddy, Vimalkumar Patel, Riley Pinkerton, Matt Pregozen, Mateen Saifyan, Pallavi Saraswati, Jay Shah, Or Sperling, Sana Surani, Rajesh Vantipalli, Avi Varadarajulu, Michelle Xu, Robbin Xu, Rui Xue, Nikki Wasikowski, Sara Wei, Feiyue Wu, Anna Zeng, and Hansen Zhang.



